Tooth decay or cavities are one of the most common health problems worldwide. They tend to affect children, as well as teenagers and older adults, but anyone can get cavities, even babies. If rotten teeth aren’t treated promptly, the cavities can soon become deeper and larger, penetrating a tooth and causing significant problems.
What Is Tooth Decay?
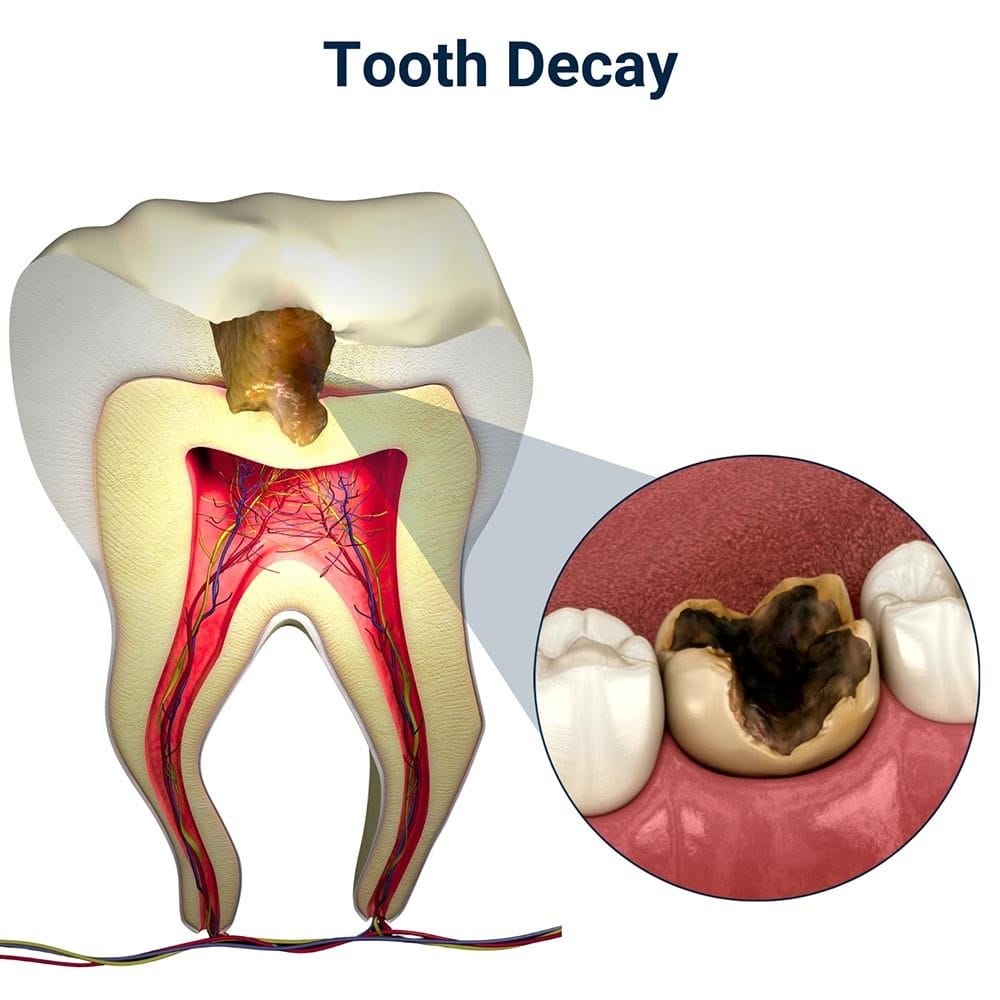 Tooth decay is when the hard outer surface of your tooth, called tooth enamel, becomes damaged, creating small openings in the enamel that allow harmful bacteria to penetrate the tooth. Directly underneath the enamel is a substance called dentin that is much softer.
Tooth decay is when the hard outer surface of your tooth, called tooth enamel, becomes damaged, creating small openings in the enamel that allow harmful bacteria to penetrate the tooth. Directly underneath the enamel is a substance called dentin that is much softer.
Dentin is made from lots of tightly packed tubules, and because these are hollow, they allow sensations to be transmitted directly to the tooth nerve right in the central part of the tooth, which is called the pulp chamber.
Initially, a cavity is small and easy to treat, but without prompt dental care, it can enlarge, weakening the tooth, so you may bite down to find the tooth literally crumbles away. An untreated cavity can cause other symptoms that become increasingly unpleasant.
How Does Tooth Decay Develop?
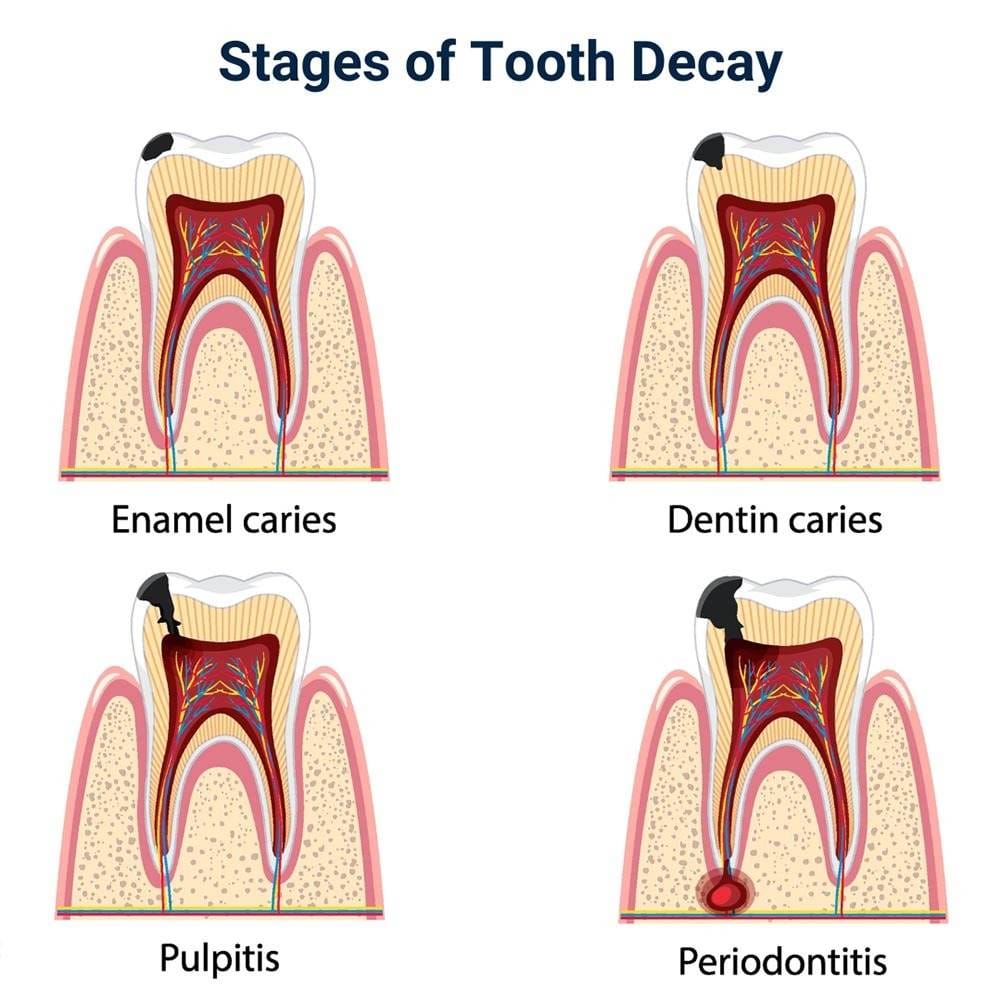 Tooth decay is a gradual process that begins with the formation of dental plaque, a sticky biofilm continually building up over tooth surfaces. The process is outlined below.
Tooth decay is a gradual process that begins with the formation of dental plaque, a sticky biofilm continually building up over tooth surfaces. The process is outlined below.
- Plaque contains bacteria, so their numbers will quickly increase unless you practice good oral care, removing dental plaque through regular brushing and flossing. Plaque bacteria feed off leftover sugars and starches trapped around your teeth after eating. They produce acid as they feed.
- The acid from bacteria softens tooth enamel by removing some of the minerals, and eventually, repeated exposure to these acids weakens the enamel to such an extent that lesions or soft spots develop in the enamel. These can soon develop into holes or cavities, resulting in tooth decay or rotten teeth. At this stage, a tooth can still be mended with an ordinary filling.
- As the hole forms, plaque bacteria can penetrate the tooth, eroding the dentin underneath so the hole deepens. When the decay reaches the pulp chamber, the tooth nerve inside becomes infected and inflamed. The infection and inflammation cause it to swell, creating pressure in the tooth and resulting in a nasty toothache.
By this stage, a tooth will need root canal therapy. Without this treatment, there is a real risk of a dental abscess or tooth loss, or the infection could affect overall health.
What Causes Tooth Decay?
Although anyone can develop a rotten tooth, certain factors can increase the risk. These include:
Tooth Location
Your back teeth, called molars and premolars, are more likely to develop cavities due to their design. Their chewing surfaces have grooves and fissures that can trap food and plaque bacteria. Sometimes, these grooves are especially deep and trickier to keep clean.
Specific Foods and Beverages
Some foods and beverages, like anything sweet, are more likely to cause cavities as these sugars feed the bacteria that cause decay. Other foods that stick to your teeth are also more harmful; the longer food remains on your teeth, the higher the risk of cavities.
Snacking Between Meals
Snacking on sugary, sticky, or carbohydrate-rich foods between meals raises your risk of tooth decay. Typically, your mouth is more acidic for up to an hour after eating these foods. The more often you snack, the longer your mouth remains acidic and the greater the damage to the tooth.
Xerostomia
This condition causes a dry mouth, where you don’t have enough saliva to wash away harmful sugars and bacteria. The drier conditions allow bacteria to thrive. Xerostomia can be a side effect of certain medications or medical treatments like chemotherapy.
Acid Reflux
Acid reflux or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD) causes strong stomach acids to flow up from the stomach into your mouth. The acids can erode tooth enamel, causing substantial damage, including tooth decay.
Eating Disorders
Problems like bulimia and anorexia, where people may vomit frequently, can also expose teeth to strong stomach acid. An eating disorder can also affect saliva production.
Poor Oral Hygiene
A lack of oral care is probably the most common reason for cavities. Allowing plaque to build up increases the exposure of your teeth to acids created by the bacteria within it. Also, plaque hardens into tartar within a couple of days, and tartar enables more plaque to stick to teeth more easily, exacerbating the problem.
What Are the Symptoms of Rotten Teeth?
Untreated rotten teeth can cause a range of symptoms, including the following.
Tooth Sensitivity
One early symptom of tooth decay is noticing increased tooth sensitivity. Eating anything sweet or sour or hot or cold may cause the tooth to twinge uncomfortably. The sensitivity can develop into pain that may only be present when you bite down on the tooth, can be continuous, or may come and go. The pain can feel sharp or throbbing.
Visible Pits or Holes in Your Teeth
If you look at the tooth, you may see a visible hole or pit, indicating a cavity. Other signs include staining, which may be white when a cavity initially develops and ranging through to brown or black as the cavity worsens.
Bad Breath
Tooth decay won’t do much for your breath, and you may develop persistent halitosis or bad breath. Brushing your teeth or using mouthwash will only provide temporary relief.
Unpleasant Taste
Untreated cavities can result in an unpleasant taste, especially if the cavity spreads to the pulp chamber, eventually resulting in a dental abscess. An abscess creates pus that can build up around the affected tooth. You might notice a pimple on the gum nearest the tooth where the pus has begun to collect. If the pimple bursts, the pus can taste extremely unpleasant.
Changes to Your Bite
A worsening cavity almost certainly means the tooth has lost a substantial part of its original structure. Eventually, as the decay continues, it can even become loose in its socket, causing changes to its position in your mouth. Loose teeth can affect your bite or occlusion, and there is a risk that the tooth may even fall out.
What Are the Potential Dangers of Rotten Teeth?
One immediate danger is tooth loss. Without treatment, a small cavity could become a more substantial problem requiring tooth extraction. There is also a risk that a cavity could create a severe infection like a dental abscess that may become life-threatening in the worst case.
This is because the infection can spread from the tooth into your facial structure and, on rare occasions, could even reach the brain or enter your bloodstream and cause significant health problems.
A severe tooth infection can need emergency dental care. Symptoms to look out for include:
- Fever
- Feeling very unwell
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck
- Facial swelling
If you recognize any of these symptoms in yourself or in someone close by, don’t delay; contact your emergency dentist immediately. If you can’t get hold of a dentist quickly, then go to your nearest emergency room.
Your dentist or physician can provide immediate care to drain the infection and alleviate pain. Unfortunately, at this stage, you will probably need strong antibiotics to try to control the infection and will almost certainly need to have the tooth removed.
Diagnosing Rotten Teeth
If you see a dentist regularly, they will check your teeth carefully for any signs of cavities. They are looking for any white spots or early signs of lesions that indicate a softer area of tooth enamel. If you haven’t been to the dentist for a while but think you have a cavity, your dentist will examine your mouth visually, ask about your symptoms, and carefully probe your teeth.
They will take dental x-rays that show the location of any cavities and the extent of the damage. The next stage is to decide on a suitable treatment.
Treating Rotten Teeth
You can treat rotten teeth in several ways depending on the decay’s seriousness. Treatment options include:
- Fluoride treatment. An early sign of a cavity that is just a soft spot or small lesion in a tooth can sometimes be reversed with topical applications of professional-strength fluoride. Your dentist will apply the fluoride directly to the tooth as a varnish, gel, or foam. Fluoride helps to re-harden tooth enamel, preventing the cavity from worsening and increasing your resistance to tooth decay.
- Dental filling. Usually, a cavity is treated with a filling made from various materials. These include tooth-colored composite resin, porcelain, or, less frequently, silver-coloured amalgam.
Tooth-colored composite resin and amalgam fillings are prepared and applied chairside. Porcelain fillings are made outside the mouth and suitable for larger cavities in your back teeth. A porcelain filling is also called an inlay or onlay. - Root canal therapy. Suppose the cavity has developed into a more serious infection affecting the dental pulp. In that case, you will need root canal therapy to remove the infection by removing the pulp and all the tissues extending into the root canals in your tooth roots. If the procedure is more complex, you may be referred to an endodontist, a specialist who performs root canal treatments. Afterward, the tooth is sealed with a material called gutta-percha.
- Dental crown. If the decay is significant, especially if you need root canal therapy to clear it up, you will need a dental crown. The crown restores strength and structure to the tooth, covering it entirely so it looks and feels comfortable. It fits tightly over the tooth, preventing further infection and decay. Crowns can be made from various materials, including precious metal alloy, a precious metal alloy shell covered with porcelain, or entirely from a ceramic material.
- Tooth extraction. Removing a tooth is the last option, and your dentist will only suggest this if the tooth cannot be saved and restored. Afterward, you will need to think about how best to replace the tooth, and your dentist can discuss possible options like a bridge or dental implant.
Preventing Tooth Decay
Tooth decay might be common but can be prevented with proper oral care. Ensure you visit your dentist regularly for dental checkups and hygiene appointments. These are particularly important so your dentist can detect any early signs of tooth decay. Hygiene appointments eliminate plaque and tartar buildup and are an easy way to maintain strong, healthy teeth.
Between appointments, ensure you brush your teeth at least twice every day and floss daily. Watch your eating habits and try not to snack between meals on sugary or starchy foods. Ideally, avoid soda and energy drinks as these are high in sugars and often contain acid.
Rotten teeth aren’t just a cosmetic issue — they can lead to serious problems, including infections, tooth loss, and even damage to your jawbone. If you’re experiencing tooth pain, sensitivity, bad breath, or visible decay, it’s essential to seek dental care as soon as possible.
At LuxDen Dental Center in Brooklyn, our experienced team uses advanced diagnostic tools and gentle techniques to restore your oral health and prevent further damage. Don’t wait until the problem gets worse — call us today at (718) 717-8866 to schedule a comprehensive dental exam and get the care you deserve.
